What is a timing belt tensioner?
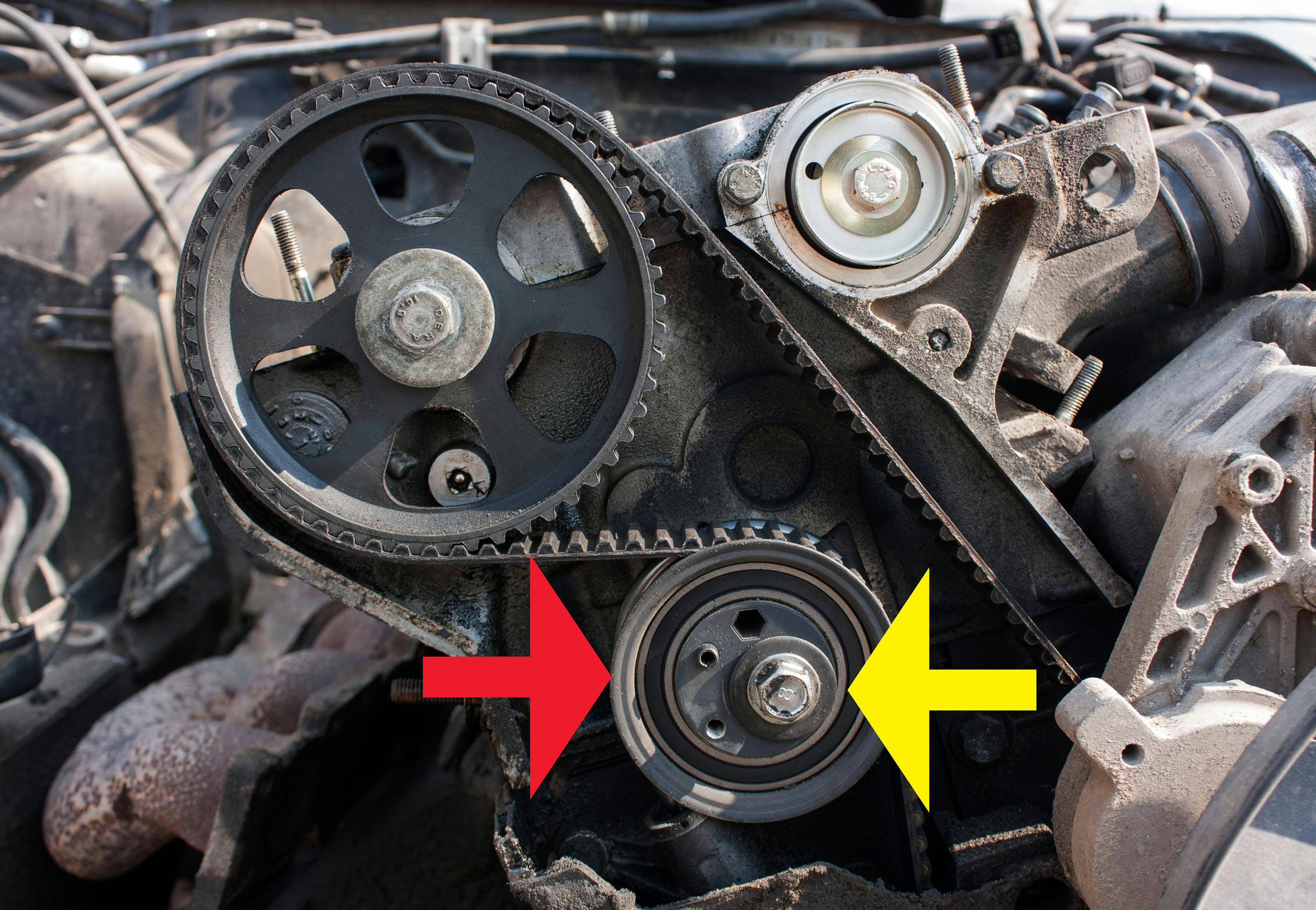
In its simplest form, a timing belt tensioner is a device that is used to both adjust a timing belt’s tension, and to maintain that tension. In this example, the tensioner is indicated by the red arrow, while the yellow arrow indicates the pensioner’s locking bolt.
In practice, timing belt tensioners vary greatly in their design. However, regardless of any given tensioners’ design, the most reliable timing belt tensioners are locked into place mechanically with bolts or nuts.
How does a hydraulic timing belt tensioner work?
In recent years, several car manufacturers have developed new types of timing belt tensioners for new engines. Let us look at one such new design-
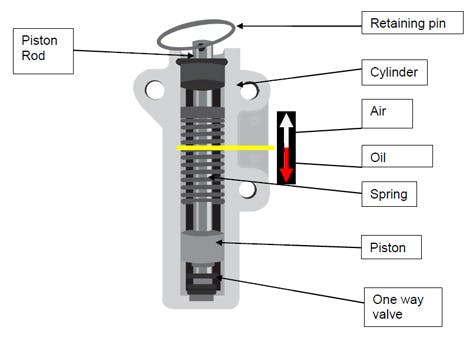
The above image shows a cut-away view of a modern hydraulic timing belt tensioner. Note that this is a generic view that does not apply to any particular vehicle.
In practice, hydraulic timing belt tensioners use pressurised engine oil to act on a piston, which is connected to the tensioner pulley with a mechanical linkage. Hydraulic belt tensioners are also self-adjusting, which means that the tensioner will automatically achieve and maintain the correct tension on the timing belt.
Claimed advantages of hydraulic timing belt tensioners over conventional tensioners include the following-
- Increased timing belt life
- Increased timing belt tensioner life
- Reduced engine noise levels
- Reduced engine vibration levels
However, it is not possible to retrofit older engines to work with hydraulic timing belt tensioners. This is because new engines incorporate dedicated oil passages to supply the tensioner with pressurised oil. Older engines simply do not have these oil passages.
